Project information
- Category: Deep Learning, Computer Vision, Medical Image Classification, Convolutional Neural Networks, Residual Networks (ResNet)
- Project date: January, 2025
- GitHub: COVID-19 Radiography
Introduction
This project focuses on developing a deep learning model for the automated classification of chest X-ray images to identify COVID-19 and other pulmonary conditions. Using convolutional neural networks (CNNs), the model can distinguish between:
- COVID-19
- Normal
- Lung Opacity
- Viral Pneumonia
The system aims to provide a reliable, fast, and accessible diagnostic tool that can assist healthcare professionals in screening patients, especially in resource-limited settings where radiologists may not be readily available.
Rapid and accurate diagnosis of COVID-19 is crucial for effective patient management and controlling the spread of the disease. While RT-PCR tests are the gold standard, they can be time-consuming and may have supply limitations. Chest X-rays, already commonly used for respiratory disease screening, offer a complementary diagnostic approach when integrated with AI analysis.
Objective
The primary objectives of this project were to:
- Develop a high-accuracy deep learning model for classifying chest X-rays into COVID-19, normal, lung opacity, and viral pneumonia categories
- Implement appropriate preprocessing techniques to enhance model performance
- Optimize the model architecture to achieve high classification accuracy while minimizing false negatives
- Create a system that could potentially be integrated into clinical workflows
- Contribute to the growing body of AI-based medical diagnostic tools for respiratory diseases
Process
The project followed a comprehensive methodology to develop and evaluate the deep learning model:
- Data Collection: The dataset was collected from the COVID-19 Radiography Database, a comprehensive collection of 40000+ chest X-ray images across multiple categories.
- Data Preprocessing: Images were resized, normalized, and augmented to create a robust training dataset.
- Model Architecture: A convolutional neural network was implemented with multiple convolutional layers, batch normalization, max pooling, and dense layers with dropout for regularization.
- Transfer Learning: Pretrained models were utilized as the foundation, with fine-tuning for the specific classification task.
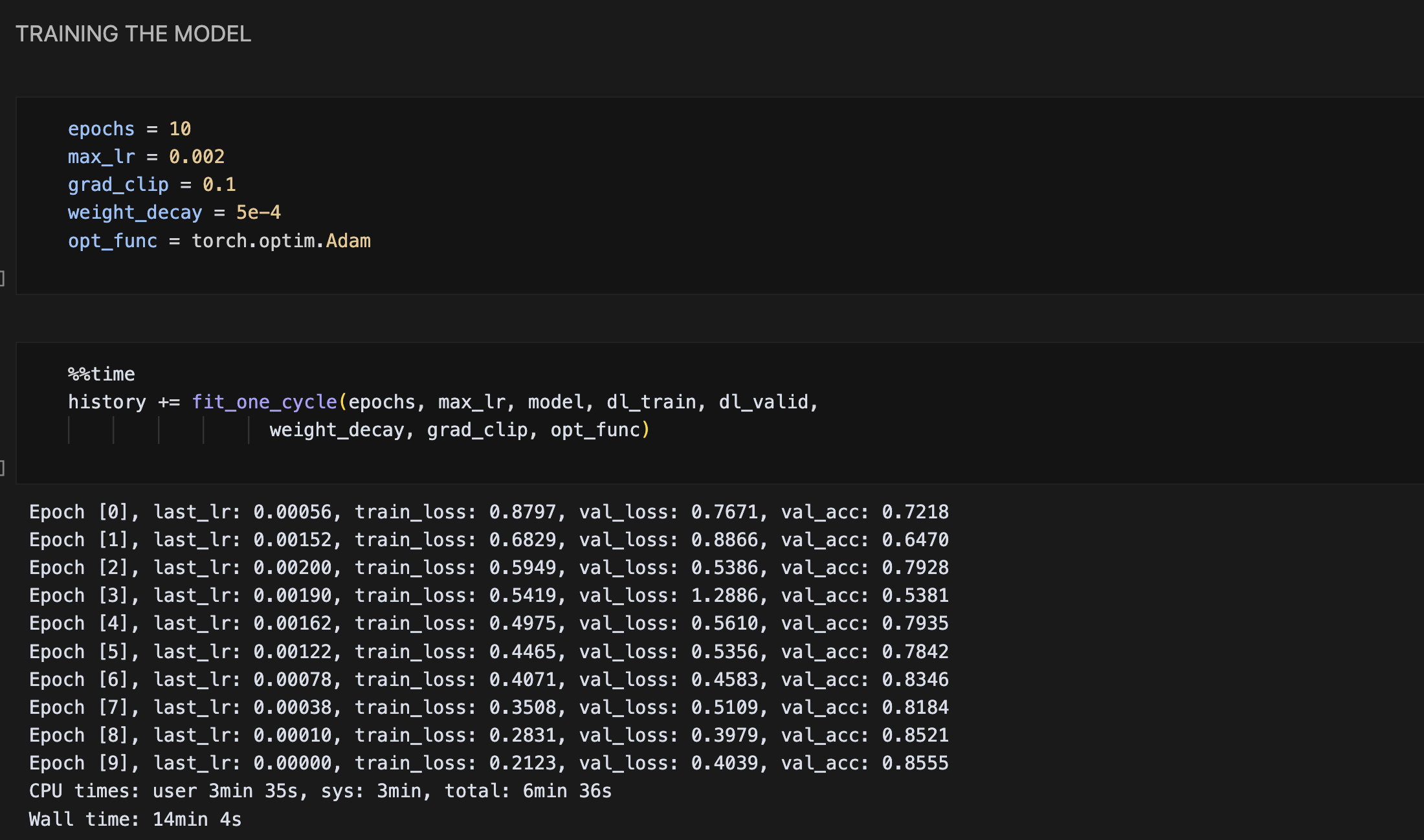
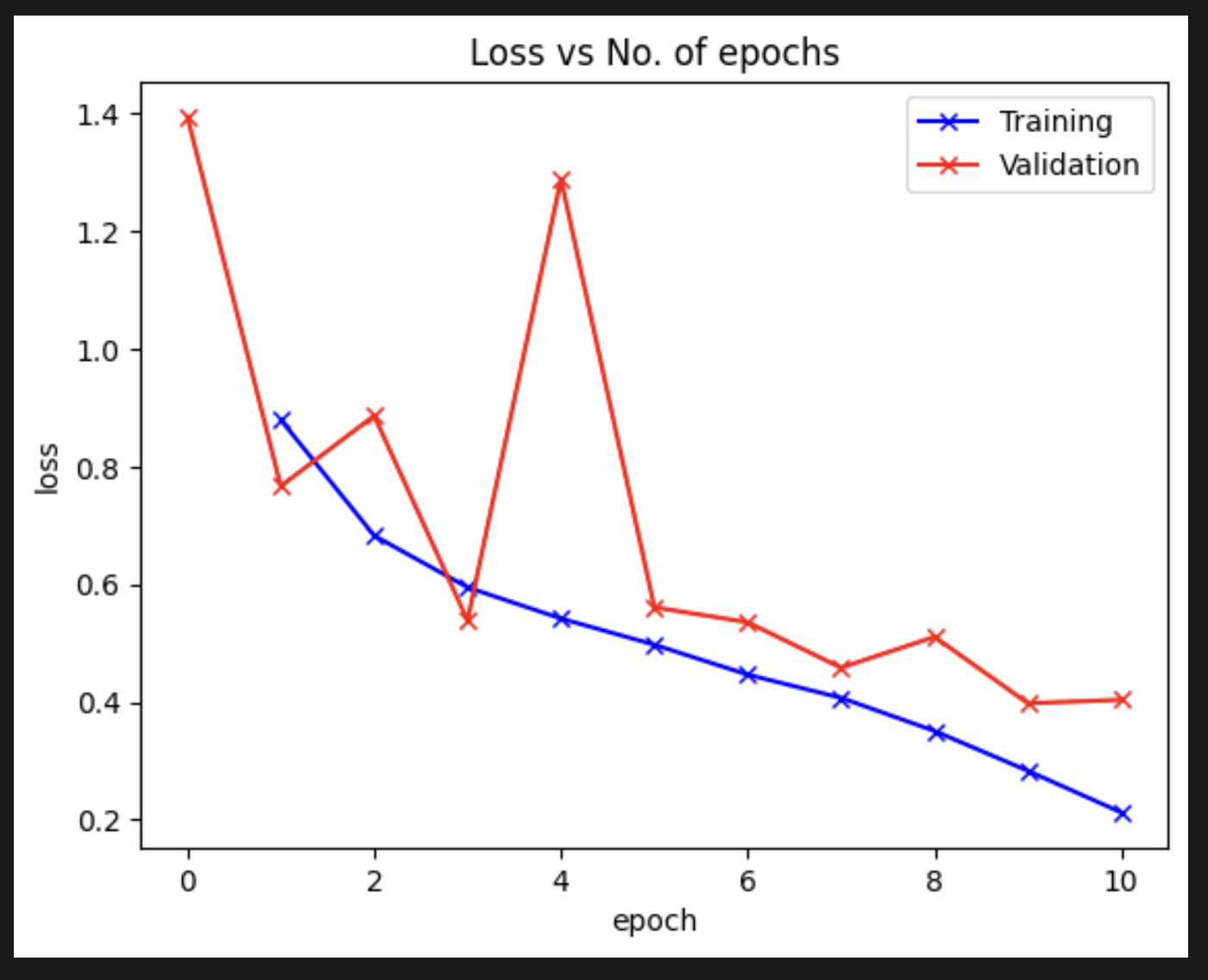
- Training: The model was trained using batch processing with appropriate learning rate scheduling and early stopping to prevent overfitting.
- Validation: K-fold cross-validation was employed to ensure model robustness.
- Hyperparameter Optimization: Grid search was used to find the best hyperparameters for the model.
- Testing: The final model was evaluated on a separate test set to assess generalization performance.
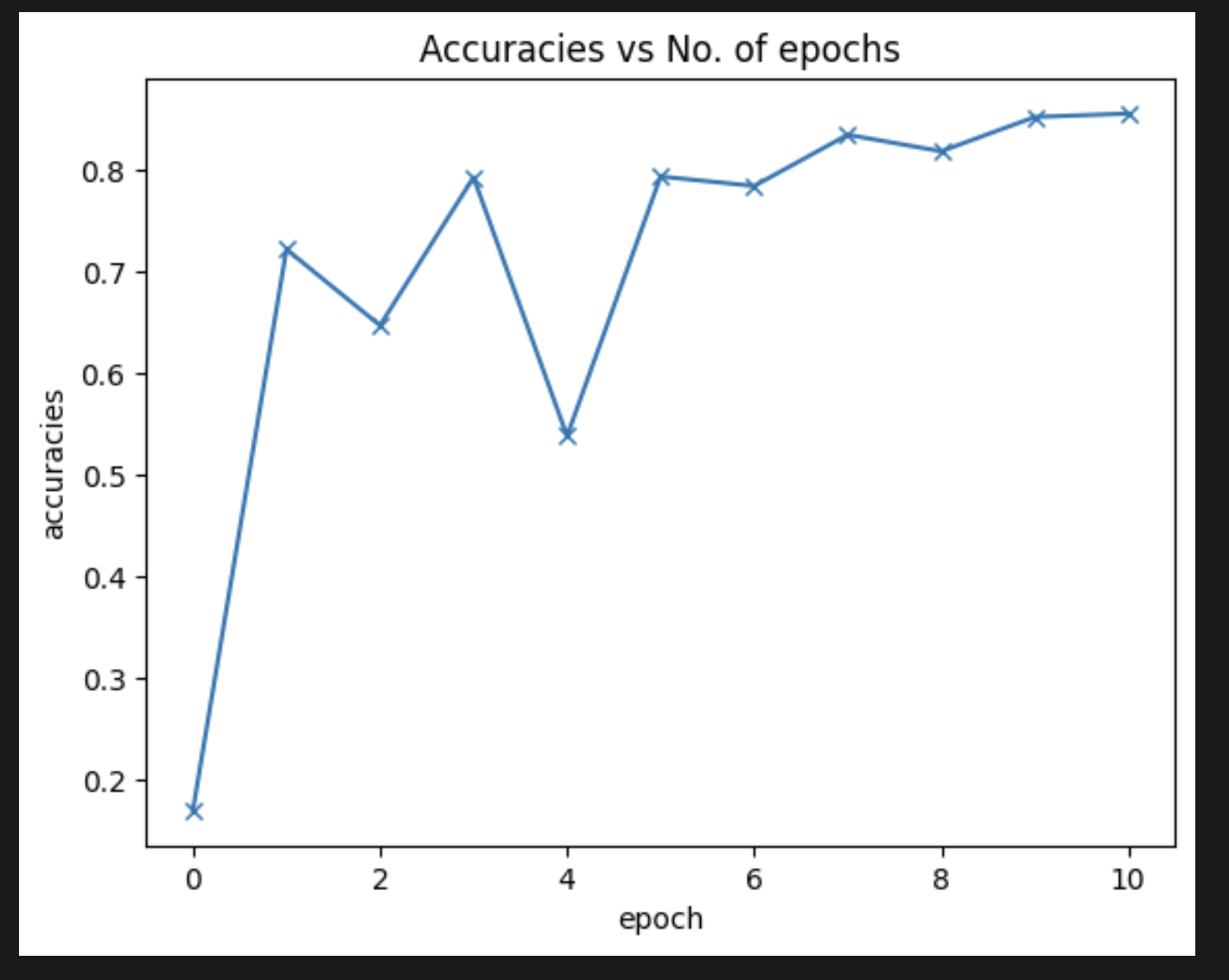
- Performance Analysis: Detailed metrics including accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and confusion matrices were generated to comprehensively evaluate model performance.
- Evaluation: The model was evaluated on a separate test set to assess generalization performance.
- Results: The model achieved impressive overall accuracy of 95% in classifying the four categories of chest X-rays.
Tools and Technologies
The project utilized a range of tools and technologies to achieve its objectives:
Platforms:
- Google Colab
- GitHub
- VS Code
Programming Language
- Python
Libraries:
- PyTorch/Torch
- Torchvision
- Opendatasets
- PIL/Pillow
- NumPy
- Pandas
- Matplotlib / Seaborn
- Scikit-learn
Deep Learning Techniques:
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
- Residual Networks (ResNet)
- Hyperparameter Optimization
- Transfer Learning
- Image Classification
Assisting our Healthcare System
This project successfully demonstrates the potential of deep learning for COVID-19 diagnosis using chest X-rays. The high accuracy and sensitivity achieved highlight the promise of AI-assisted medical image analysis in supporting healthcare professionals, especially in contexts where specialized radiological expertise may be limited.
Future directions for this research include:
- Expanding the model to detect additional respiratory conditions
- Implementing explainable AI techniques to provide insights into model decisions
- Developing a user-friendly interface for clinical deployment
- Conducting collaborative validation studies with healthcare institutions
- Exploring integration with other diagnostic modalities for comprehensive assessment
As AI continues to evolve in healthcare applications, models like this one represent important stepping stones toward more accessible, efficient, and accurate medical diagnostics.